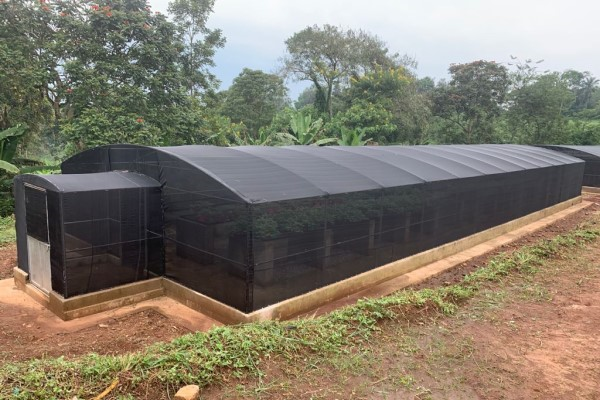

In greenhouse farming, achieving the right balance between temperature and humidity is essential for maximizing crop yield and maintaining plant health. Proper ventilation plays a critical role in creating an optimal growing environment by ensuring fresh air circulation, regulating temperature, and preventing the buildup of excess moisture. This article explores the importance of greenhouse ventilation, the methods available, and best practices for effective ventilation.
Greenhouses are designed to provide a controlled environment for plants, but without adequate ventilation, issues such as overheating, humidity buildup, and fungal diseases can arise. Proper ventilation ensures:
Natural Ventilation:
Mechanical Ventilation:
Hybrid Systems:
Conclusion:
Optimizing greenhouse ventilation is essential for creating a productive and disease-free growing environment. Whether through natural, mechanical, or hybrid systems, proper ventilation ensures crops thrive under optimal conditions, leading to better yields and healthier plants.

Challenges of Wind in African Agriculture
06 Mar 2025
Elements for Plant Nutrition in African Farming
06 Mar 2025

Optimizing Greenhouse Ventilation: Balancing Temperature and Humidity for Maximum Yield
06 Mar 2025

The Role of Trellis Twine and Clips in Vertical Farming
06 Mar 2025